 Oromandibular Dystonia PDF Download
Oromandibular Dystonia PDF Download
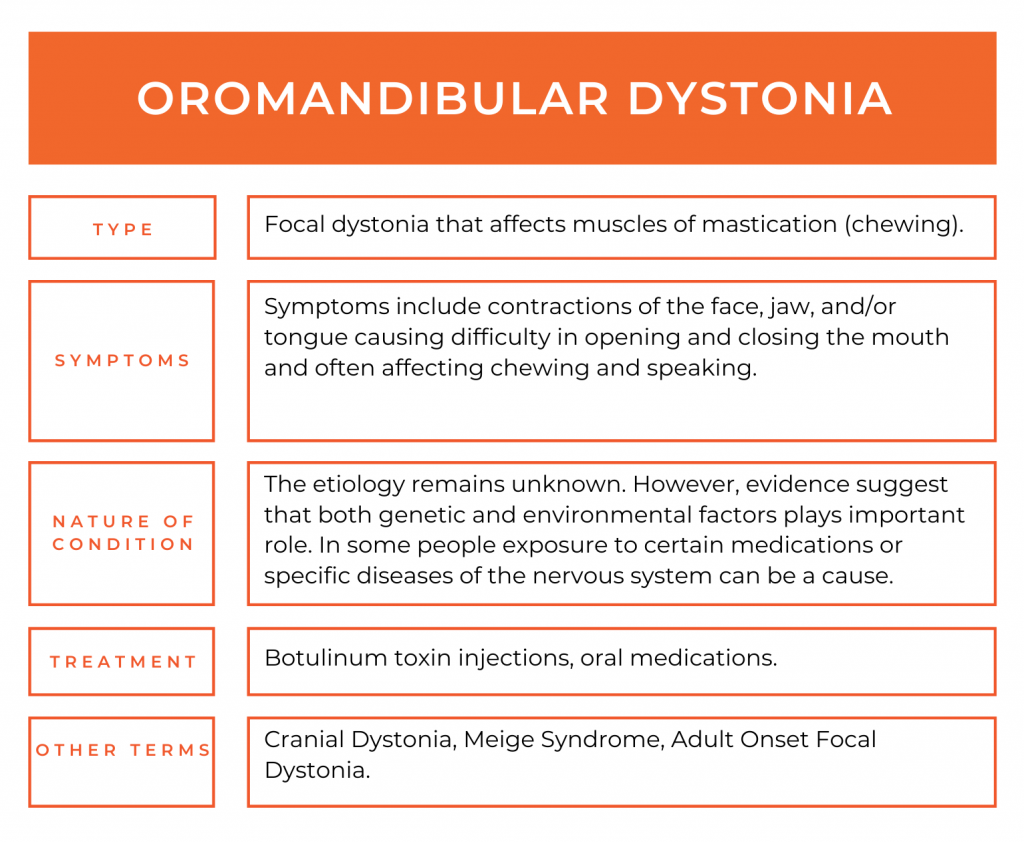
Symptoms:
Oromandibular dystonia typically presents with involuntary, sustained muscle contractions of mouth, face, and jaw. Sometimes symptoms occur only during activities such as speaking or chewing. However, sometimes activities like speaking and chewing reduce symptoms. Difficulty in swallowing may be a symptom of oromandibular dystonia if the jaw is affected or tongue is affected.
Causes:
In many people, oromandibular dystonia develops without a clear cause and is an isolated dystonia. However, some people have a specific neurological disease which causes oromandibular dystonia alongside other progressive symptoms. Examples of diseases such as this include Wilson’s disease, neuroacanthocytosis and neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation. Oromandibular dystonia may resemble tardive dyskinesia caused by long-term use of dopamine receptor blocking drugs (DRBs).
Diagnosis:
Your doctor will ask about your medical history, mainly :
- The age of onset
- The area of the body affected
- Is the condition getting worse?
- Are there any other associated clinical problems?
The doctor will also perform an examination of the affected body part(s). For some patients, blood tests, electromyography or brain scanning may be recommended. However, it may not be possible for your doctor to find an exact cause.
Treatment:
Botulinum Toxin – Botulinum toxin injections can effective in the treatment of oromandibular dystonia. Botulinum toxin Type A and B have been approved for treatment of dystonia.
Botulinum toxin injections temporarily weaken muscles to decrease the contractions and usually need to be injected every 3 to 4 months to continue to have an effect. Side effects of weakness can occur, and this is particularly the case when injections are given around the mouth.
Oral Medication – The most commonly used medications include: anticholinergics (e.g. Artane -trihexyphenidyl), benzodiazepines, baclofen, muscle relaxants. Medications often are given on a trial-and-error basis, to balance between the benefits and potential side effects (dry mouth, drowsiness, anxiety and difficulty urinating).

